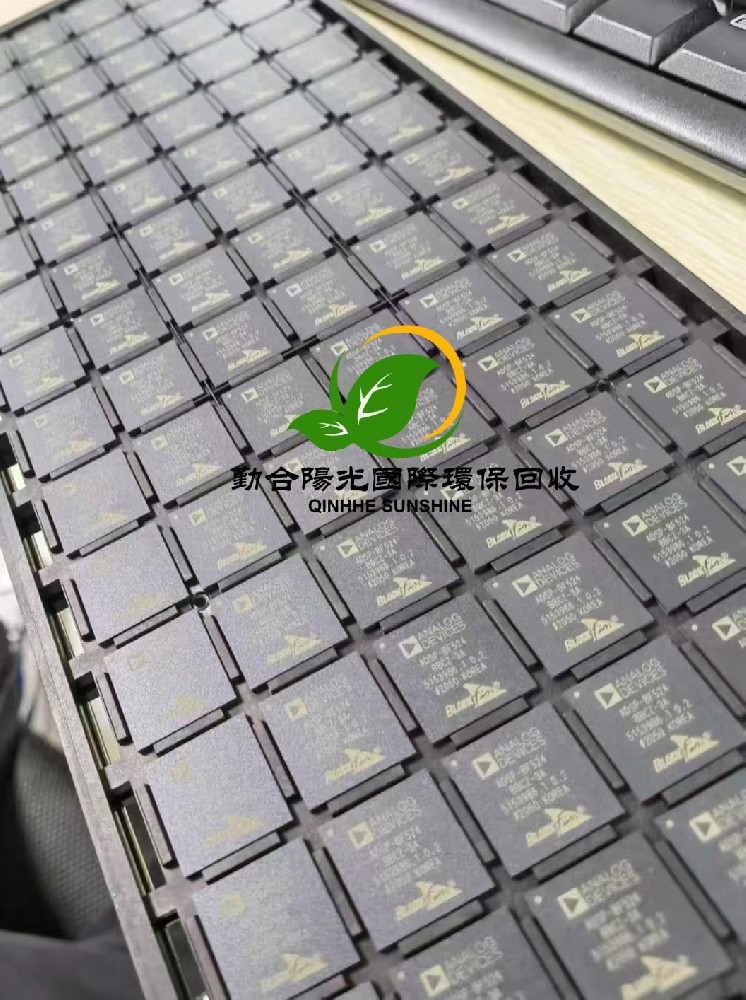
The Current Situation and Characteristics of the Chip Recycling Market
In today's era of booming digital economy, as the "brain" of modern technology, the recycling and utilization of chips has become an important issue that cannot be ignored. More than 500,000 tons of discarded chips are generated globally every year. These seemingly tiny silicon wafers contain huge economic value and environmental risks. The chip recycling market is quietly emerging, and it is expected that the global market size will reach 10 billion US dollars by 2025. This emerging market is not only related to the recycling of resources but also an important support for the sustainable development of the electronics industry.
I. The Current Situation and Characteristics of the Chip Recycling Market
The global chip recycling market is showing a rapid growth trend. The North American and European markets are relatively mature, with a relatively complete recycling system established. Due to the large consumption of electronic products, the Asia-Pacific region has become the fastest-growing market. As the world's largest production base for electronic products, China has great potential in the chip recycling market.
The main participants and business models are becoming increasingly diversified. Traditional electronic waste recycling enterprises are transforming towards specialization, chip design and manufacturing enterprises are starting to lay out recycling businesses, and emerging Internet recycling platforms are rising rapidly. The business model extends from simple material recycling to high-value-added services such as data erasure and component remanufacturing.
The main challenges faced by the market include: scattered recycling channels, high technical thresholds, and great cost pressure. At the same time, chip recycling also faces important opportunities: resource shortages drive the growth of recycling demand, technological progress reduces recycling costs, and environmental protection policies create market space.
II. Technological Innovation and Industrial Upgrading in Chip Recycling
Chip disassembly and classification technologies are developing towards intelligence. Technologies such as laser cutting and robotic arm disassembly have improved the disassembly accuracy, and machine vision and artificial intelligence technologies have realized the automatic identification and classification of chips. These technological advancements have greatly improved the recycling efficiency and quality.
Data erasure and security protection technologies are becoming increasingly important. With the improvement of data security requirements, chip recycling must ensure the complete erasure of data. New data erasure technologies can completely wipe out stored data, and blockchain technology can track the entire process of chip recycling to ensure data security.
The recycling industry chain is upgrading towards the high-end. It extends from simple material recycling to high-value-added links such as component remanufacturing and chip refurbishment. Some enterprises have started to provide professional services such as chip performance testing and quality certification, promoting the recycling industry to climb towards the high end of the value chain.
III. The Future Development Trends of the Chip Recycling Market
The market demand will continue to grow. The development of new technologies such as 5G and the Internet of Things will bring more chip demands, and at the same time, it will also generate more discarded chips. It is expected that the global chip recycling market will maintain an average annual growth rate of more than 15% in the next five years.
Policies and regulations will be more perfect. Countries are formulating stricter regulations on electronic waste management to promote the development of the chip recycling industry. The extended producer responsibility system will prompt chip enterprises to participate more in recycling businesses.
Technological innovation will drive industrial transformation. New technologies such as artificial intelligence and blockchain will reshape the chip recycling model. Intelligent recycling systems will improve recycling efficiency, digital platforms will optimize resource allocation, and new technologies will create new business models.
The chip recycling market is in a period of rapid development, facing a situation where opportunities and challenges coexist. Through technological innovation, model innovation, and institutional innovation, the chip recycling industry is expected to become a new growth point in the digital economy era. This is not only a business opportunity but also an important way to achieve the sustainable development of the electronics industry. Let's open up this "urban gold mine" together with a more open vision and more innovative thinking and contribute to the green development of the digital economy.
The Recycling Value of Scrap Metals: The Economic and Environmental Significance of Resource Reuse
Introduction
Scrap metal recycling refers to extracting valuable metal materials from discarded metal products and reinvesting them into the production process. With the increasingly serious global problems of resource shortages and environmental pollution, scrap metal recycling has not only become an important economic activity but also an important way to achieve sustainable development. This article will explore the value of scrap metal recycling, influencing factors, and its positive significance for the economy and the environment.
I. The Value of Scrap Metal Recycling
1. Resource Conservation
Metals are non-renewable resources, and the mining and smelting of new metals require a large amount of energy and natural resources. By recycling scrap metals, the dependence on primary ores can be reduced, and the service life of resources can be extended.
2. Economic Benefits
Scrap metal recycling has significant economic value. Take common scrap metals as examples:
• Scrap copper: The recycling price is about 50-60 yuan per kilogram (market price in 2023).
• Scrap aluminum: The recycling price is about 15-20 yuan per kilogram.
• Scrap steel: The recycling price is about 2-4 yuan per kilogram.
Recycling enterprises can obtain considerable profits by processing and selling scrap metals.
3. Environmental Benefits
The processes of metal mining and smelting will generate a large amount of pollutants, such as carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and heavy metal wastewater. The energy consumption and pollution of scrap metal recycling are much lower than those of primary metal production, which helps to reduce carbon emissions and environmental pollution.
II. Factors Affecting the Recycling Value of Scrap Metals
1. Metal Types
There are large differences in the market prices of different metals. Precious metals (such as gold, silver, and platinum) and rare metals (such as copper and nickel) have higher recycling values, while the recycling values of common metals (such as iron and aluminum) are relatively lower.
2. Metal Purity
The purity of scrap metals directly affects their recycling value. High-purity scrap metals are easier to process and reuse, so their prices are higher. For example, the recycling price of pure copper wires is higher than that of copper products mixed with other materials.
3. Market Supply and Demand
Metal prices are affected by the global market supply and demand relationship. When the demand for a certain metal is strong, its recycling price will also rise. For example, the rapid development of the electric vehicle industry has pushed up the demand for copper and nickel, thus increasing the recycling values of these metals.
4. Recycling Technology
Advanced recycling technologies can improve the extraction efficiency and purity of metals, thereby increasing the recycling value. For example, the efficiency of recycling precious metals by electrolysis is much higher than that of the traditional chemical dissolution method.
5. Policy Support
The environmental protection policies and subsidy measures of the government will also affect the economics of scrap metal recycling. For example, some countries encourage enterprises to carry out scrap metal recycling businesses through tax incentives or subsidies.
III. The Main Types and Values of Scrap Metal Recycling
1. Scrap Copper
Copper is an important industrial metal and is widely used in fields such as wires, cables, and electronic components. The recycling value of scrap copper is relatively high, especially for high-purity copper wires and copper pipes.
2. Scrap Aluminum
Aluminum is lightweight and corrosion-resistant and is often used in packaging, construction, and automobile manufacturing. The energy consumption of recycling scrap aluminum is only 5% of that of primary aluminum production, which has significant economic and environmental benefits.
3. Scrap Steel
Steel is an important material for infrastructure construction. The recycling of scrap steel can greatly reduce the energy consumption and pollution in the processes of iron ore mining and steelmaking.
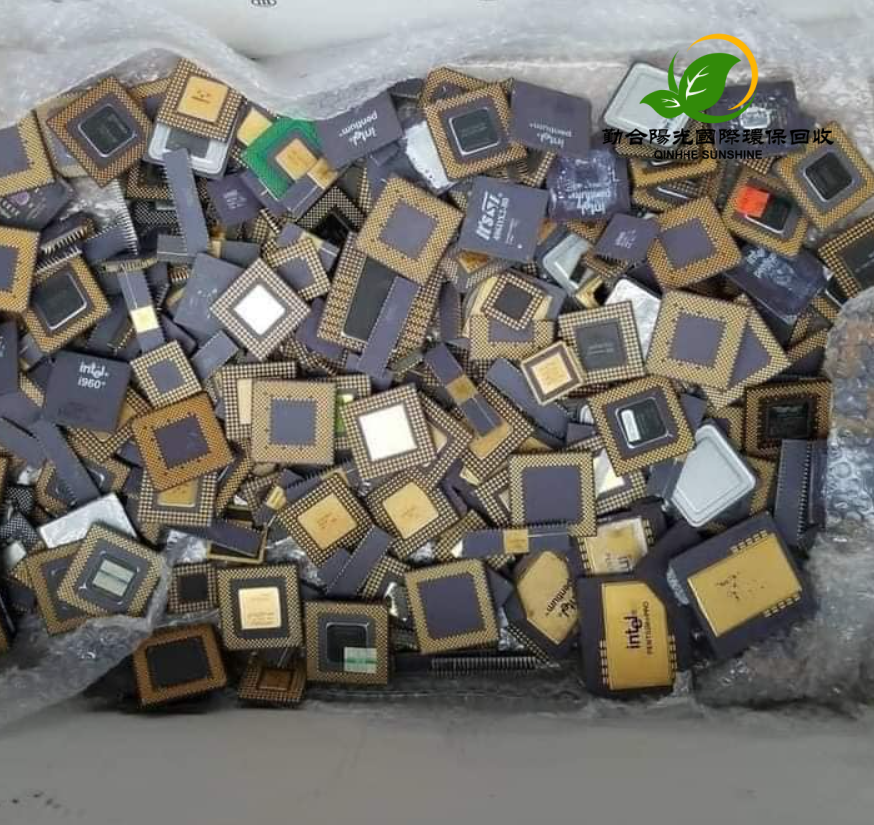
4. Precious Metals
Precious metals such as gold, silver, and platinum have become the key objects of scrap metal recycling due to their rarity and high value. Electronic waste (such as discarded mobile phones and computers) is an important source of precious metal recycling.
5. Rare Metals
Rare metals such as nickel, cobalt, and lithium have important applications in the new energy and high-tech industries. With the rapid development of these industries, the recycling values of rare metals are constantly increasing.
IV. The Process Flow of Scrap Metal Recycling
1. Classification and Sorting
The first step in scrap metal recycling is to classify and sort according to the types and purities of metals. This process can be completed manually or by automated equipment.
2. Crushing and Cleaning
Crush the scrap metals into small pieces and remove surface oil stains, paints, and other impurities through cleaning.
3. Smelting and Purification
Send the processed scrap metals to a furnace for smelting to remove impurities and improve the metal purity. Precious metals and rare metals usually require further purification by electrolysis or chemical methods.
4. Molding and Reuse
The purified metals can be cast into ingots, bars, or other shapes and reinvested in industrial production.
V. The Economic and Environmental Significance of Scrap Metal Recycling
1. Promote the Circular Economy
Scrap metal recycling is an important part of the circular economy. Through the closed-loop model of "resources-products-recycled resources", it reduces resource waste and environmental pollution.
2. Create Employment Opportunities
The scrap metal recycling industry chain involves multiple links such as collection, sorting, processing, and sales, creating a large number of employment opportunities for society.
3. Reduce Carbon Emissions
The energy consumption of recycling scrap metals is much lower than that of primary metal production. For example, the energy consumption of recycling aluminum is only 5% of that of primary aluminum production, and the recycling of each ton of scrap aluminum can reduce about 9 tons of carbon dioxide emissions.
4. Protect the Ecological Environment
Metal mining and smelting will cause serious damage to the ecological environment, such as deforestation, soil erosion, and heavy metal pollution. Scrap metal recycling can reduce the mining of natural resources and protect the ecological environment.
VI. The Future Trends of Scrap Metal Recycling
1. Technological Innovation
With the progress of science and technology, scrap metal recycling technologies will be more efficient and environmentally friendly. For example, artificial intelligence and robot technologies can improve the sorting efficiency, and green chemical technologies can reduce the pollution in the recycling process.
2. Policy Support
Governments of various countries will continue to introduce policies to support the scrap metal recycling industry, such as increasing recycling targets, providing financial subsidies, and tax incentives.
3. Enhancement of Public Awareness
With the enhancement of environmental protection awareness, the public will pay more attention to the classification and recycling of scrap metals, promoting the improvement of the recycling rate.
Conclusion
Scrap metal recycling not only has significant economic value but also has important significance for environmental protection and resource conservation. Through technological innovation, policy support, and public participation, the scrap metal recycling industry will迎来a broader development prospect and make important contributions to achieving the sustainable development goals. In the future, scrap metal recycling will become the mainstream method of resource utilization, bringing double benefits to the economy and the environment.
我的WhatsApp:69536972-郵箱:martin.hyq88@gmail.com香港回收销毁免费咨询热线:13377641657香港电话:00852-69536972,期待您的来电,共同开启环保与价值并存的新篇章!


 繁體中文
繁體中文 简体中文
简体中文 English
English



 咨询热线
咨询热线 公司邮箱
公司邮箱 地址导航
地址导航