Waste Recycling: Embarking on a New Journey of Resource Circulation
In the current situation where resources are limited and the pressure on environmental carrying capacity is increasing, the field of waste recycling, with its unique value, has become a crucial part of sustainable development. It is not only a secondary exploration of waste but also a vivid practice of the concept of resource recycling.
Diverse Fields of Waste Recycling
1. Metal Recycling: Metals play a key role in modern industry, and the recycling of waste metals is of great significance. For example, steel, as a metal with a huge consumption, after being recycled and remelted, can be largely invested in industries such as construction and machinery manufacturing. Recycling waste steel for steelmaking can significantly reduce the amount of iron ore mining, and decrease energy consumption and environmental pollution. Another example is copper. Due to its excellent electrical conductivity, it is widely used in the electronics field. After the copper in waste wires, cables, and electronic components is recycled and refined, it can be remade into the conductive components of various electronic products, achieving efficient resource circulation.
2. Plastic Recycling: Plastic products are everywhere in our lives, and the recycling of waste plastics is extremely urgent. Common plastics such as polyethylene and polypropylene can be made into recycled plastic products after recycling, such as plastic pipes and plastic furniture. Some technologically advanced enterprises can even convert waste plastics into fuel, realizing the recycling of energy. However, plastic recycling faces challenges such as the complexity of plastic types and difficulties in separation, which require continuous technological innovation to solve.
3. Paper Recycling: Paper is a commonly used item in daily life and office work. After recycling waste paper, through processes such as deinking and pulping, it can be remade into various types of paper. After one ton of waste paper is recycled, about 800 kilograms of recycled paper can be produced, saving a large amount of wood resources and energy, and at the same time reducing water pollution in the papermaking process. However, paper recycling also has problems such as an imperfect recycling system and uneven paper quality.
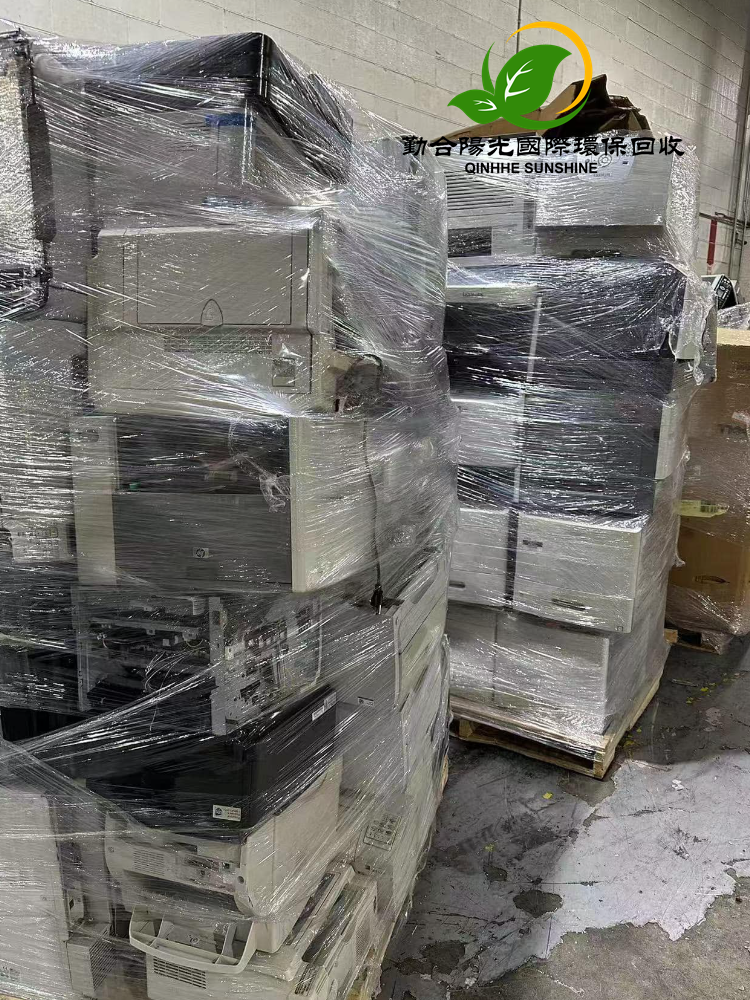
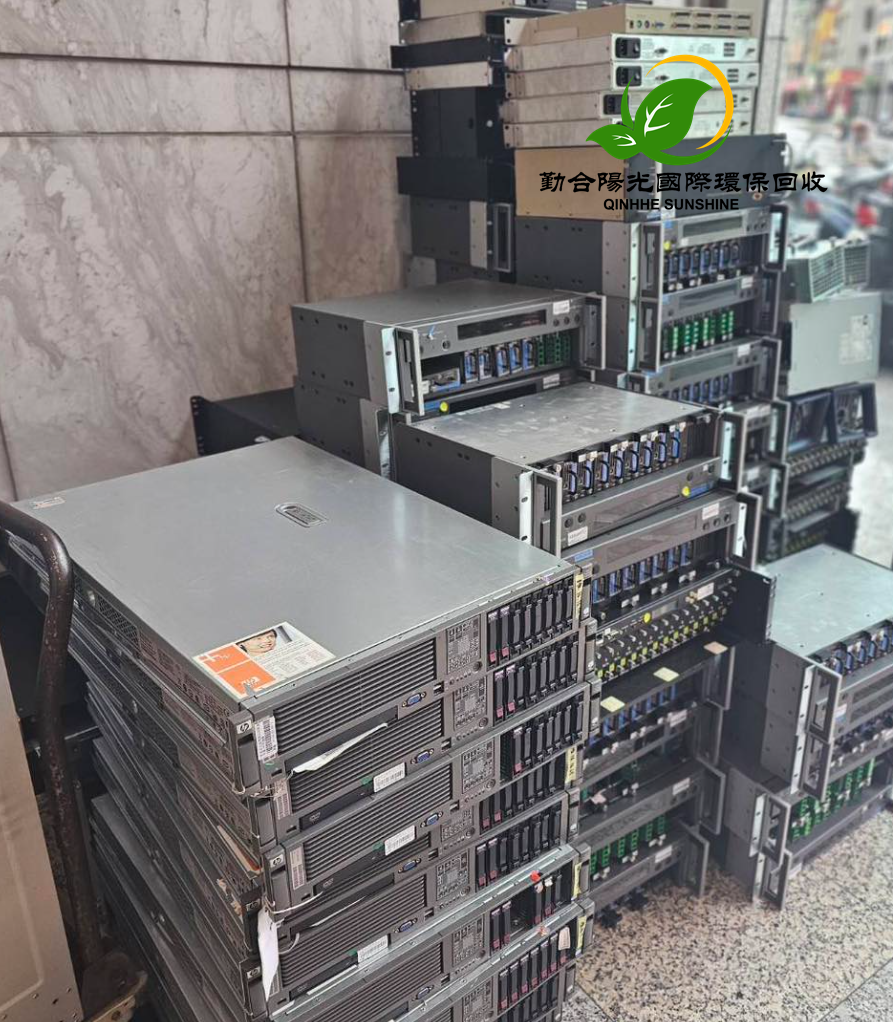
4. E-waste Recycling: With the development of science and technology, electronic products are updated rapidly, and the amount of e-waste has surged. In old mobile phones, computers and other electronic devices, there are recyclable materials such as metals like copper, gold, and silver, as well as plastics and glass. Recycling e-waste reasonably can not only obtain valuable resources but also prevent harmful substances such as lead and mercury from polluting the environment. However, the recycling and disassembly of e-waste require professional technology and equipment, and the current industry standardization still needs to be strengthened.
Challenges Faced by Waste Recycling
1. Imperfect Recycling System: In many areas, especially in rural and remote areas, the layout of waste recycling outlets is unreasonable, and there is a lack of a systematic recycling network. Residents who want to dispose of waste items often don't know where to put them. At the same time, the recycling channels are scattered, and there is a lack of effective connection between individual recyclers, small recycling stations, and large recycling enterprises, resulting in low recycling efficiency.
2. Limited Technical Level: The recycling and utilization of some waste items are technically difficult. For example, for some composite materials and new plastics, the existing technology is difficult to efficiently separate and reprocess them. The various components and materials in e-waste are complex, and the technology for accurately extracting valuable components also needs to be improved. Technical bottlenecks limit the recycling rate and added value of waste items.
3. Weak Public Awareness: Some members of the public have insufficient awareness of the importance of waste recycling and lack the habits of garbage classification and resource recycling. It is common to discard waste items casually, resulting in recyclable resources being mixed into the garbage and being landfilled or incinerated, causing a waste of resources.
Significance of Waste Recycling
1. Resource Conservation: The resources on the earth are limited, and waste recycling can effectively alleviate resource shortages. By recycling waste metals, plastics, paper, etc., the exploitation of primary resources can be reduced. For example, recycling aluminum can save 95% of the energy used in the production of primary aluminum, greatly reducing the dependence on resources such as bauxite.
2. Environmental Protection: If waste items are not properly disposed of, they will seriously pollute the environment. For example, the heavy metals in waste batteries seep into the soil and water sources, endangering the ecology and human health. Waste plastics are difficult to degrade in the natural environment, forming "white pollution". Recycling and treating them reasonably can avoid these pollutions and protect the ecological environment.
3. Creation of Economic Value: The waste recycling industry can create economic benefits. Recycling and processing enterprises can make profits by processing waste items into recycled products and selling them. This industry also drives the development of upstream and downstream industries, such as the manufacturing of recycling equipment and the sales of recycled products, creating a large number of job positions and promoting economic growth.
Strategies for Promoting the Development of Waste Recycling
1. Improve the Recycling System: The government should make overall plans, rationally arrange recycling outlets, and build a complete recycling network with community recycling stations as the foundation, sorting centers as the support, and large processing enterprises as the leading entities. Encourage enterprises to carry out the "Internet + Recycling" model, and use online platforms to facilitate residents to hand over waste items, improving recycling efficiency.
2. Strengthen Technological R&D: Increase investment in the research and development of waste recycling technology, and encourage cooperation between scientific research institutions and enterprises. Set up special scientific research funds to support the research of key technologies such as the separation of composite materials and the efficient disassembly of e-waste. Establish technology demonstration bases to promote advanced recycling technologies and equipment.
3. Enhance Public Awareness: Popularize waste recycling knowledge and environmental protection concepts through various channels, such as television, the Internet, and community publicity. Carry out environmental protection-themed activities, such as garbage classification competitions and creative production of waste items, to improve public participation and enthusiasm.
Waste recycling is a cause that benefits both the present and the future. Although it faces challenges, as long as all parties work together to improve the recycling system, enhance the technical level, and strengthen public awareness, waste resources can be revitalized, injecting strong impetus into the sustainable development of the earth.
我的WhatsApp:69536972-郵箱:martin.hyq88@gmail.com


 繁體中文
繁體中文 简体中文
简体中文 English
English



 咨询热线
咨询热线 公司邮箱
公司邮箱 地址导航
地址导航